A company (business or professional practice) frequently need funding to maintain its business operations or fill a brief working capital shortage. When this happens, the company raises money using one of two approaches. One of the most popular ways to finance a business is through debt. It offers the fewest hassles and is quick and simple. We will learn what debt finance is in this essay, how it functions, and its benefits and drawbacks.
What is debt financing?
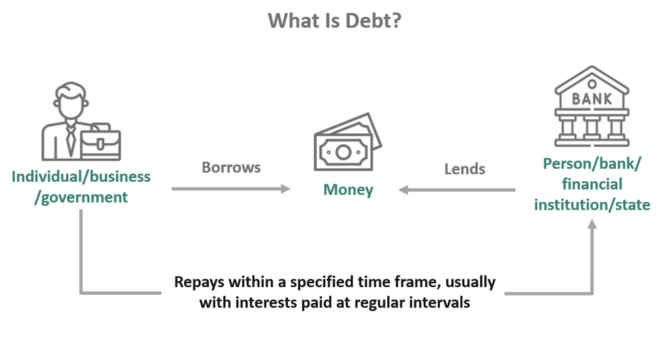
- Debt financing is the process of borrowing money from a source (often a bank or a Non-Banking Finance Company – NBFC or even the general public) with the commitment to pay it back with interest, within the specified tenure at the pre-decided rate of interest.
- While we generally think of only banks and NBFCs as the source of debt financing, companies raise funds from the general public as well. This is done through the issuance of bonds, commercial papers, debentures, etc.
- Debt financing involves the raising of funds from a lender and paying back in EMIs. Hence, it is a prudent practice to check certain things related to your business before you decide on debt financing. You need to check the duration for which you need the funds, the cash flows generated from these funds, etc.
How does debt financing work?
For the borrower, debt financing works just like a regular debt. The borrower (a company in this case) applies for the loan either from a bank, NBFC or the general public. The terms of the loan are fixed. These include:
- Loan amount – the amount which is being borrowed. This needs to be calculated by the borrower based on the requirement and affordability.
- Tenure – the duration for which the loan is being taken. The tenure needs to be comfortable – neither so long that the borrower gets into a debt trap nor too short that the EMI amount is too high.
- Rate of interest – the rate at which the borrower will return the loan amount, in the form of an interest payment. The borrower needs to find a lender (or a suitable instrument) that charges an affordable rate of interest.
Different types of debt financing
There are different variations in which debt financing can be classified. Some of the common ways of debt financing are mentioned below:
Based on the collateral requirement:
- Secured – loans that require collateral
- Unsecured – loans that do not require collateral
Based on the functionality:
- Installment loans – these are regular term loans, that are borrowed from a bank or NBFC and repaid in EMIs.
- Revolving credit – type of credit facility that allows a borrower to borrow money, use it to fund the business needs, repay it and borrow it again whenever required.
- Cash flow loans – an unsecured loan which is used to meet a shortfall in working capital.
Based on the lender:
- Bank/NBFC loans – these are typically term loans, the most common form of debt financing.
- Debentures – these are long or short-term loans that are not backed by any collateral but rely on the creditworthiness of the borrower/issuer.
- Bonds – these are generally long-term loans that are backed by collateral.
Advantages and disadvantages of debt financing
Debt financing is a great way for a business to leverage a small amount and generate a large amount by investing the same in business operations. Hence, debt financing can be good or bad, depending on how the debt is used, treated and serviced.
Advantages of Debt Financing:
- It is a great way to leverage a small amount and use it to generate a much larger amount from business operations.
- Debt payments are often tax-deductible, unlike other forms of raising funds.
- Since the monthly repayment is known beforehand, it is easier to plan for debt repayment over the entire tenure of the loan.
- A consistent debt repayment over the tenure of the loan helps build a good credit score for your business.
- Debt financing does not result in dilution of stake for the promoter(s).
- This form of financing is less costly compared to equity financing, despite the real “cost” of equity not being very apparent.
- Debt, once repaid is “over”, unlike equity which could remain perpetually “ongoing”.
Disadvantages of Debt Financing:
- Depending on the type of debt, many lenders could ask for collateral. This could be an uncomfortable proposition for a borrower.
- In businesses where cash flows are irregular or uncertain, servicing a fixed amount every month by way of EMIs could get difficult.
- A wrongly borrowed or wrongly serviced loan can adversely affect your credit score or credit rating.
Conclusion
As you can see, the advantages of debt financing far outweigh the disadvantages. Hence, it makes sense to avail of debt from a good lender, so that you can take your business to greater heights. If you need a good source of debt financing for your business, you can avail of a Business Loan from Credit Success. We have an extremely hassle-free application process, easy eligibility criteria, attractive interest rates, flexible repayment tenure and best-in-class customer service.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of debt financing?
Term loans, bond issuance, debentures, commercial paper and credit lines are some examples of debt financing.
How does financing with debt work?
In the case of debt financing, the borrower borrows an amount from the lender at a pre-determined rate of interest and repayment tenure. Rate of interest and tenure can change over the period of the loan. Also, the lender(s) can be Banks, NBFCs, individuals or a consortium. The loan is repaid in the form of EMIs over its tenure.
What is debt vs equity financing?
Debt financing does not result in dilution of stake for the promoter(s), while equity financing almost always results in stake dilution. Debt is repaid over a certain tenure while equity remains “unpaid” till the time the issuer buys back the equity. Also, debt has a much lower cost compared to equity.
What are the four types of debt financing?
There are many types of debt financing, as mentioned above.